Industry News
2D Fiber Arrays: The Future of Scalable Optical Sensing Solutions
In the world of modern technology, optical sensing plays a crucial role in a wide range of applications, from industrial monitoring to environmental detection. As demand for faster, more reliable, and scalable sensing solutions grows, one technology stands out as a game-changer: 2D fiber arrays. These arrays promise to revolutionize the way optical sensing systems operate by providing an efficient and scalable method for capturing and processing data at large scales. In this blog, we will explore how 2D fiber arrays are shaping the future of optical sensing, their key benefits, and why they are quickly becoming a critical component of the modern technological landscape.
What is a 2D Fiber Array?
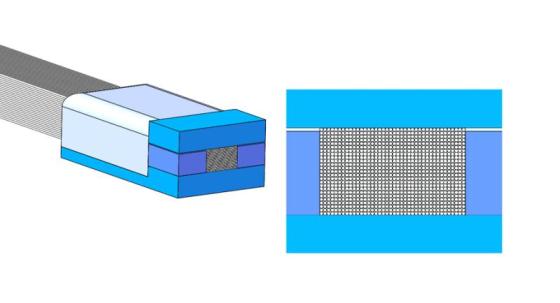
A fiber array refers to a collection of optical fibers arranged in a specific pattern to carry light signals. Typically, these fibers are bundled together to allow for efficient light transmission in applications such as telecommunications and sensing. A 2D fiber array, as the name suggests, refers to an array in which fibers are arranged in two dimensions, creating a grid-like structure. This enables the array to cover a much larger area and allows for the efficient collection of optical signals from multiple sources simultaneously.
Unlike traditional one-dimensional arrays, a 2D fiber array can support more complex sensing tasks. By integrating a larger number of fibers in two dimensions, the array can capture a broader range of data, improving the sensitivity and accuracy of the optical sensing system.
Internal Link 1: Learn more about fiber arrays and how they work here.
The Evolution of Optical Sensing Systems
Optical sensing is at the heart of many industries, including manufacturing, telecommunications, medical diagnostics, and environmental monitoring. Traditional optical sensing methods, however, often face challenges in terms of scalability, performance, and cost-efficiency. The introduction of 2D fiber arrays is addressing these issues by providing a scalable solution that can handle high volumes of data while maintaining accuracy and reliability.
A typical fiber optic sensing system relies on the ability to measure light transmitted through fiber-optic cables. As such, fiber optics are essential to the operation of these systems. The 2D fiber array is the next step in advancing the performance of optical sensing systems by enabling the simultaneous measurement of multiple points in a given environment.
Internal Link 2: Discover scalable and efficient optical solutions here.
Benefits of 2D Fiber Arrays in Optical Sensing

The adoption of 2D fiber arrays in optical sensing applications brings several advantages:
1. Scalability
One of the most significant benefits of 2D fiber arrays is their scalability. Traditional optical sensing systems are often limited by the number of fibers they can accommodate. A 2D fiber array, however, allows for the integration of a larger number of fibers, thereby increasing the system’s sensing capacity. This makes it possible to scale up the sensing network without compromising performance.
For instance, in industrial applications, such as temperature monitoring or structural health monitoring, 2D fiber arrays can be deployed over large areas to capture data from numerous points simultaneously. This scalability allows businesses to gather more data in real time, leading to better decision-making and enhanced efficiency.
2. Enhanced Sensitivity and Accuracy
With more fibers integrated into the array, 2D fiber arrays can offer higher sensitivity and accuracy. By positioning fibers across a larger area, the array can collect data from a broader range of sources, improving the resolution of the sensing system. This is particularly useful in applications such as environmental monitoring, where precise measurements of various factors like air quality, temperature, or pressure are required.
3. Improved Data Processing Efficiency
Since a 2D fiber array can collect data from multiple points simultaneously, it can streamline the data processing workflow. The system can analyze large datasets in real time, making it possible to detect anomalies or trends much faster. This enhanced data processing capability is critical in fields such as telecommunications, where quick responses are required to ensure the smooth operation of networks.
Internal Link 3: See how optical sensing is revolutionizing industries here.
Applications of 2D Fiber Arrays in Various Industries
The use of 2D fiber arrays is becoming more prevalent across various sectors. Below are some of the key industries benefiting from this technology:
1. Telecommunications
In the telecommunications industry, optical fibers are the backbone of high-speed internet and data transmission. 2D fiber arrays are used to enhance the performance of optical networks by increasing data throughput and reducing signal loss. By enabling large-scale deployment of optical fibers in two-dimensional arrays, providers can ensure faster and more reliable connections.
2. Healthcare and Medical Diagnostics
In medical diagnostics, optical sensing is used for non-invasive monitoring of patients' health. 2D fiber arrays are ideal for applications such as endoscopy or imaging, where high-resolution data from multiple sources is required. The ability to collect data from numerous points at once allows for more accurate diagnostic results and better patient care.
3. Environmental Monitoring
Environmental sensors are often deployed in harsh or remote locations to monitor factors such as air quality, temperature, or radiation levels. The scalability of 2D fiber arrays makes them perfect for large-scale environmental sensing networks. They can be deployed across vast areas to monitor multiple environmental parameters simultaneously.
Internal Link 4: Explore more about fiber-optic sensing applications here.
How Does Optical Fiber Encode Data?
At the core of fiber-optic data transmission is the principle of encoding data using light signals. Fiber optics rely on light signals to transmit information over long distances with minimal loss. This makes fiber optics ideal for high-speed communication networks, including internet and telecommunication systems.
In fiber-optic systems, data is encoded using light pulses that travel through the fibers. The light signals can be modulated to carry digital information, with different types of encoding techniques employed depending on the system's requirements. Fiber-optic cables can handle large amounts of data at high speeds, making them essential for modern communication systems.
Internal Link 5: Learn how fiber optics encode data here.
What is the Difference Between Optical Fiber and Fiber Optic?
The terms optical fiber and fiber optic are often used interchangeably, but there is a subtle difference. Optical fiber refers to the actual physical fiber made of glass or plastic that transmits light. On the other hand, fiber-optic generally refers to the technology and systems that use optical fibers for communication or sensing purposes.
The main difference is that optical fibers are the individual components, while fiber-optic systems encompass the complete setup, including fibers, transmitters, receivers, and other essential components used to transmit light-based data.
Internal Link 6: Explore the technology behind fiber optics here.
Future of 2D Fiber Arrays in Optical Sensing
As the demand for scalable and efficient optical sensing solutions grows, 2D fiber arrays are set to play a crucial role in the future of various industries. With their ability to provide high-performance sensing over large areas, they are expected to be integral to advancements in telecommunications, healthcare, environmental monitoring, and industrial applications.
The continued development of 2D fiber arrays will further enhance the precision, scalability, and efficiency of optical sensing systems. This, in turn, will open up new opportunities for businesses and organizations to deploy large-scale, real-time sensing networks that can address a wide range of challenges.
Internal Link 7: See how the future of optical sensing is shaping industries here.
Conclusion
In conclusion, 2D fiber arrays are transforming optical sensing by providing scalable, efficient, and high-performance solutions. From industrial applications to environmental monitoring, their ability to capture and process data from multiple points simultaneously makes them a critical tool in the advancement of modern technology. As we continue to push the boundaries of optical sensing, 2D fiber arrays will undoubtedly play a key role in shaping the future of data acquisition, processing, and analysis.
By embracing the power of fiber optics and 2D fiber arrays, industries can unlock new possibilities and achieve better outcomes in terms of performance, scalability, and cost-efficiency. It’s clear that 2D fiber arrays are not just a technological innovation—they are the future of scalable optical sensing solutions.
Latest News
-
How Fiber Grating Technology Is Shaping Modern Optical Systems
2025-05-07 -
The funny team building activity in Yilut - Your hard work is more beautiful than the scenery.
2024-10-25 -
YILUT Shines at ECOC EXHIBITION 2023 - We Look Forward to Your Visit!
2023-09-27 -
【CIOE2023】Yilut Tech Invites You to Shenzhen International Optoelectronics Exhibition - A Journey with Light!
2023-08-23 -
Embracing Infinite Possibilities: YILUT Showcasing New Products at NETCOM2023 Exhibition
2023-07-25


